Everyone has a door somewhere in their house, right? It’s a great subject to practice drawing.
I’m sure you have a door almost exactly like this one somewhere in your house. It’s commonplace, but it’s also a series of repeating shapes that can teach you a lot about perspective.
I left it slightly ajar, but it doesn’t have to be. Seat yourself as far away as you can get from it. The closer you are, the more difficult it is to keep your measurements straight. I’d like you to sit at a slight angle to it so you can think about perspective.
This is intended to be a fast drawing, taking you no more than 15 or 20 minutes. The same rules apply to a careful drawing, of course; you’d just be more meticulous in your measuring and marking. But you’ll learn just as much going fast.
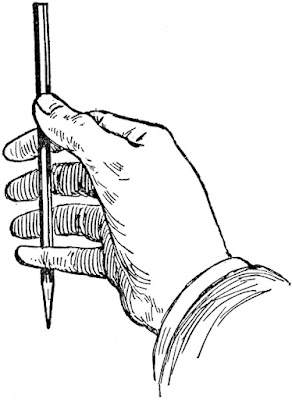
My first task is to figure out the angles of the top and bottom of the door. (My camera distorts perspective so what’s in the photo won’t match what’s on my drawing.) I do that by holding my pencil along the bottom of the door and figuring out the angle.
I find that setting my pencil down on my paper at the appropriate angle helps me see it better.
Then I do the exact same thing on the top.
Note that the shelf at my eye level is completely horizontal. Any level surface at eye level has to be horizontal; that’s a hard-and-fast rule.
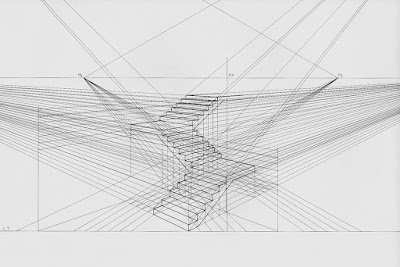 |
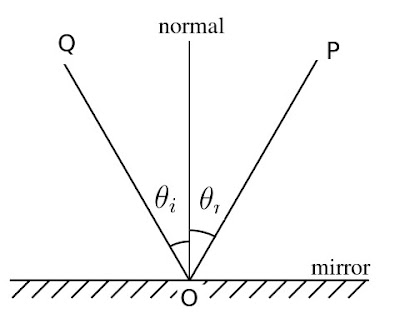
| Two-point perspective, courtesy Luciano Testoni. All those lines traveling off to the vanishing points on the left and right? Let’s call them rays. |
|
The picture above is classical two-point perspective with a lot of extra bells and whistles. I don’t want you to get bogged down in it; I included it so you can compare the rays in that drawing to what you see in your room. Notice that when you look at lines high in your room, the ‘rays’ travel downward to the sides, where the so-called ‘vanishing points’ are. When you look at objects near the floor, the rays travel upward to the vanishing points. That’s because the vanishing points are always at the viewer’s eye level.
 |
| My measuring hashmarks |
Next, I do that
nifty measuring thing that involves holding my pencil in front of my eye and using it as a ruler. Since the height is already determined by my angled lines, I just need to figure out how wide the door is relative to the height. I figured the door is a little less than half as wide as it was tall. Later, I’ll find out just how off I was.
This shape is called a trapezoid, and there’s an easy way to find its center. Just draw an X from corner to corner as shown. That’s very useful information in perspective drawing, because it helps you place windows, doors, roof peaks, etc. correctly. Make a habit of finding it.
And here’s a quick-and-dirty way to get the perspective right. Divide the two side lines into equal units—thirds, quarters, eighths, or whatever other units you can mark off by eye. Then just draw lines connecting the corresponding sides. The 1/3 point on the left gets attached to the 1/3 point on the right, etc. You’ll have the perspective rays right in one try.

I never get my measurements right on the first try, so I’ve learned to not fuss too much on my initial measurements. The great thing about repeating shapes is that your mistakes are easy to see. I realized the door was slightly too short and wide, so I adjusted them slightly. I also took out the free-hand curl on the right-bottom corner. Note how useful the center point is in placing the central spine of the door. I know that the moulding around the glass is the same width all around, so this is one of those repeating shapes I can use to check my work. (Of course, it’s going to be ever so slightly wider on the side closer to me.)
No, I can’t draw a straight line, not without a ruler.
My finished drawing. I would have enjoyed putting in all the details, and I could always be more careful, but I still have letters to write. You can finish it or not, to your heart’s content.
Next week, I’m going to have you draw a pie plate. That means you have to finish up the leftover pie before Monday. And a reminder, you can post your homework
here. There are lots of people reading
Monday Morning Art School; I’d love to see some drawings!